HISAKO International is an ISO 9001 and MSME certified manufacturer and global exporter of rice, spices, pulses, and value-added food products. Based in India with global operations, we deliver lab-tested, food-safe products through reliable internat...
- (+91) 9538000215
- hisako.intl@aol.com
- 1101, West, Rajajinagar, , Bengaluru, Karnataka, India. 560010
© 2020 Hisako International OPC pvt ltd. All Rights Reserved
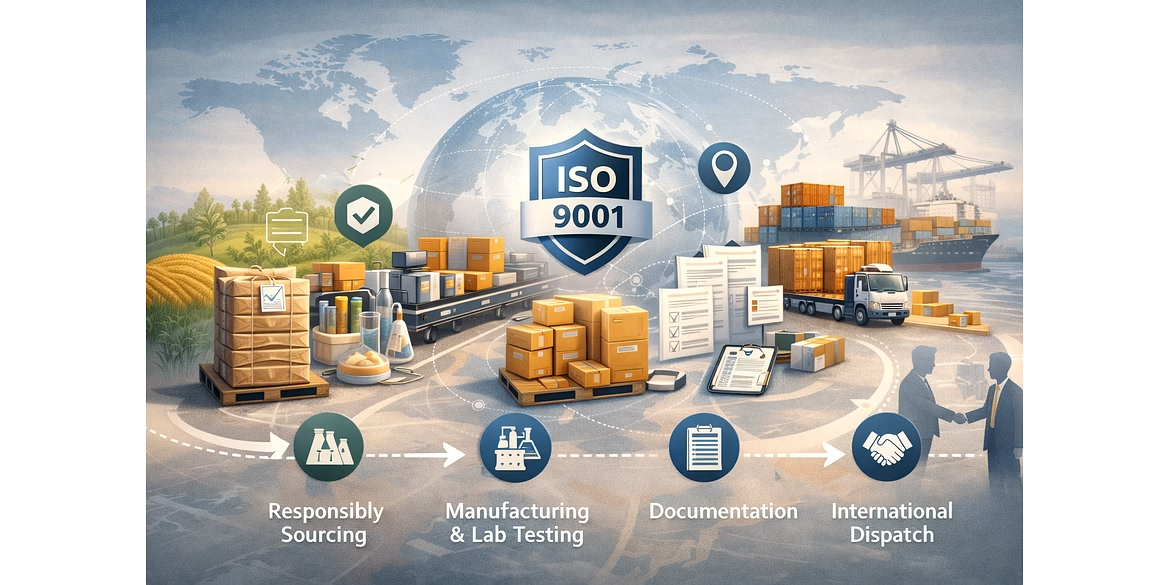

For global importers and international buyers, one of the biggest risks in agri and food trade is export complexity. Delays, documentation errors, compliance gaps, or inconsistent coordination can disrupt supply chains and significantly increase costs.
This is why experienced buyers prioritize exporters who offer end-to-end export management—a structured approach that controls every stage from sourcing to international dispatch. This article explains how a well-managed export process works and why it is critical for reliable global food trade.
End-to-end export management refers to a fully integrated export process where the exporter controls, coordinates, and documents every stage of the supply chain. Instead of relying on multiple intermediaries, the exporter acts as a single point of responsibility.
For importers, this approach delivers:
• Fewer handovers
• Lower risk of errors
• Better visibility and accountability
• Predictable delivery timelines
An exporter with true end-to-end capability manages quality, compliance, documentation, and logistics under one coordinated system—reducing risk and complexity for global buyers.
Export reliability begins at the sourcing stage. Raw materials must meet quality, safety, and regulatory requirements before they enter the production cycle. Weak sourcing controls can compromise the entire export process.
Key sourcing practices include:
• Procurement from verified and compliant suppliers
• Quality screening of raw materials
• Alignment with food safety and export standards
• Documentation for traceability
Strong sourcing controls reduce downstream risks and create a stable foundation for consistent global food exports.
Once sourced, products move into manufacturing and processing under ISO 9001-compliant systems. These standardized workflows ensure repeatability and consistency across export batches.
Manufacturing controls typically include:
• SOP-driven processing workflows
• Controlled handling and processing environments
• Batch identification and documentation
• Hygiene and safety compliance
This stage ensures products meet buyer specifications and international quality benchmarks before moving further in the export cycle.
Before export, products undergo rigorous quality control and lab testing. This stage is critical for regulatory approval, food safety assurance, and buyer confidence.
Quality assurance activities include:
• Batch-level inspections
• Lab testing for safety and quality parameters
• Verification against customer requirements
• Pre-dispatch quality clearance
Lab-tested shipments significantly reduce the risk of rejection or non-compliance at destination ports.
Export packing and labeling must meet international food regulations and destination-specific requirements. Errors at this stage can delay or block shipments entirely.
Export readiness includes:
• Hygienic and secure packing
• Correct labeling as per destination norms
• Batch and traceability markings
• Preparation of shipment-ready consignments
Attention to detail at this stage ensures smooth customs clearance and faster international dispatch.
Documentation is one of the most complex areas of global trade. End-to-end exporters manage this process internally to avoid errors, gaps, or inconsistencies.
Key export documentation includes:
• Quality and compliance certificates
• Lab test reports
• Commercial invoices and packing lists
• Regulatory and customs documents
Accurate documentation prevents delays, penalties, and compliance issues at destination ports.
Efficient logistics coordination is essential for timely international dispatch. End-to-end exporters plan and manage containerization, freight, and scheduling internally.
Logistics management includes:
• Container planning, including mixed 20-foot containers
• Secure container loading
• Freight coordination and scheduling
• Dispatch tracking and updates
Strong logistics planning ensures shipments move reliably from origin to destination.
The final stage involves shipment dispatch, tracking, and coordination with buyers and logistics partners to ensure a smooth handover.
Post-dispatch support includes:
• Shipment tracking and status updates
• Coordination with buyers and logistics partners
• Documentation support during customs clearance
• Resolution of transit-related queries
Strong coordination ensures continuity, transparency, and trust between exporter and importer.
For importers, working with exporters who manage the entire process simplifies procurement and significantly reduces operational risk.
Key benefits include:
• Lower compliance and documentation risk
• Predictable delivery timelines
• Consistent quality across shipments
• Reduced coordination effort
• Stronger long-term partnerships
1. What does end-to-end export management mean for buyers?
It means the exporter manages the complete process—from sourcing and manufacturing to documentation, logistics, and international dispatch—reducing buyer risk and effort.
2. Why is end-to-end management important in food exports?
Food exports involve strict quality, safety, and regulatory requirements. Integrated management ensures compliance and consistency at every stage.
3. Does end-to-end export management reduce shipment delays?
Yes. Centralized control over documentation, quality checks, and logistics significantly reduces delays and errors.
4. How does lab testing fit into the export process?
Lab testing is conducted before dispatch to verify safety, quality, and compliance with destination market requirements.
5. Can exporters support mixed commodity shipments?
Yes. End-to-end exporters can efficiently manage mixed container shipments, optimizing cost and logistics for buyers.
6. How does documentation management benefit importers?
Accurate documentation ensures faster customs clearance and reduces regulatory risk at destination ports.
7. Is end-to-end export management suitable for long-term sourcing?
Absolutely. It provides consistency, scalability, and reliability—key requirements for long-term global supply partnerships.

